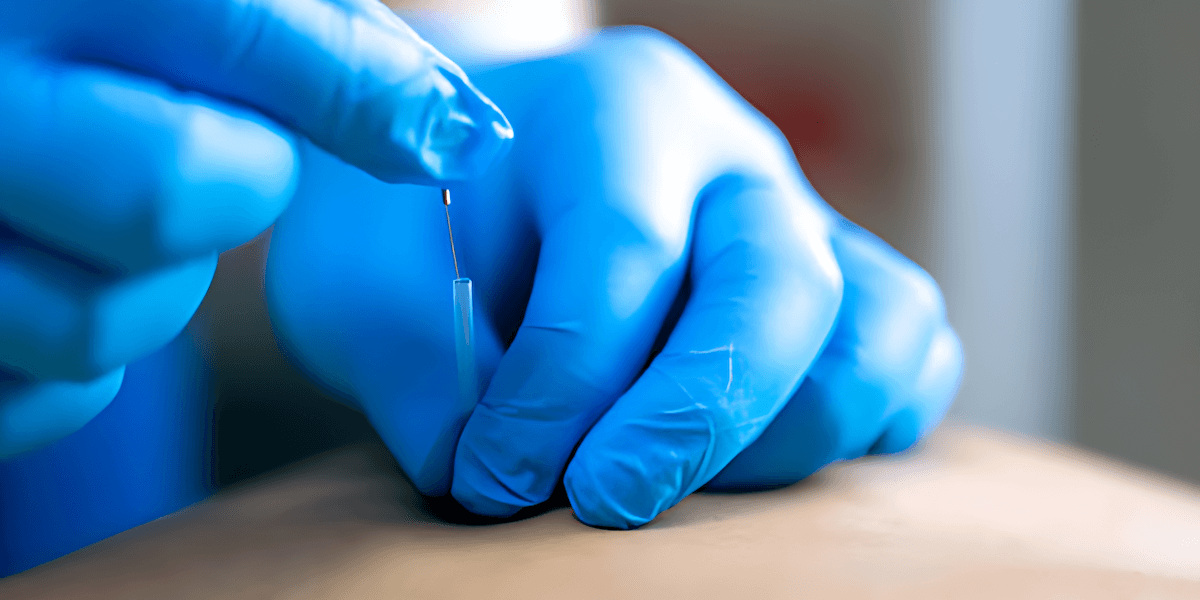
Dry needling is a therapeutic technique used in physiotherapy to treat musculoskeletal pain, muscle tightness, and trigger points. It involves the insertion of thin, sterile needles directly into the skin and muscle tissues to target specific points of discomfort, known as myofascial trigger points.
How Dry Needling Works:
- Needle Insertion: A fine, sterile needle is inserted into the skin and muscle tissue at the site of muscle tightness or a trigger point. These points are areas where muscle fibres are tight, contracted, or knotted.
- Muscle Stimulation: The insertion of the needle causes a local twitch response, which is a brief contraction of the muscle. This reaction helps to release the tight muscle fibres, improving blood flow and reducing muscle spasms.
- Pain Relief: By deactivating trigger points and promoting muscle relaxation, dry needling helps reduce pain, improve mobility, and increase range of motion.
Conditions Treated with Dry Needling:
- Muscle spasms and stiffness
- Chronic muscle pain
- Tension headaches
- Neck and back pain
- Tendonitis
- Sports injuries
- Sciatica
- Repetitive strain injuries
Benefits of Dry Needling:
- Pain Reduction: Helps decrease pain and muscle discomfort, often providing immediate relief.
- Improved Range of Motion: Alleviates tightness and stiffness in muscles, leading to better flexibility and mobility.
- Faster Recovery: Facilitates quicker recovery from injuries by improving muscle function and circulation.
- Non-invasive: Unlike injections or surgery, dry needling is a minimally invasive procedure with few risks.
What to Expect During Treatment:
- The therapist will first assess the muscle or area causing pain.
- A sterile needle is then inserted at the trigger point, which might cause a mild discomfort or sensation, such as a muscle twitch or slight ache.
- After the treatment, patients may experience temporary soreness, similar to post-exercise muscle soreness, which typically resolves within a few hours to a day.
Dry needling is often combined with other physiotherapy treatments, such as stretching exercises, manual therapy, or strengthening exercises, for the best results. It is most effective when used as part of a comprehensive rehabilitation program.